In the face of an ever-increasing global population set to surpass 9 billion by 2050, agriculture and science have converged to create sustainable, innovative solutions to food production. Cellular agriculture is perhaps the most cutting edge of them all.
Producing meat, poultry and seafood through cellular agriculture promises to revolutionize the way we think about, grow and consume food. When rolled out to consumers in the coming years, these products are expected to have the same nutrition profile and organoleptic properties as their conventionally sourced counterparts. Organoleptic properties refer to the sensory aspects of food, including taste, sight, smell, and touch.
What is Cellular Agriculture?
Cellular agriculture refers to the production of agricultural products from cell cultures. Through cellular agriculture, meat, poultry, and fish can be produced ex vivo, or grown outside the animal. The finished product – commonly referred to as cultured, clean or cell-based meat – replicates the characteristics of muscle harvested from food-producing animals.
How Are Cell-Cultured Foods Made?
The production process is quite complex and varies across producers. At a high level, there are four core elements to production: (1) cell cultures, (2) scaffolds, (3) media and (4) bioreactor (cultivator).
Cells are obtained from food-producing animals, healthy at the time of biopsy. The cells are subsequently separated and transferred in a sterile environment and placed in a bioreactor also referred to as a cultivator. Once placed in the cultivator, the cell cultures are fed nutrients referred to as media. Media is a mixture of ingredients that works as a food source for cell lines. The cultivator controls food supply inputs and temperature, the cells are continuously monitored, and once the meat is cultivated, meat tissues are harvested and stored under appropriate conditions. See Figure 1, below (P.D. Edelman, D.C. McFarland, V.A. Mironov, and J.G. Matheny. Tissue Engineering. May 2005).
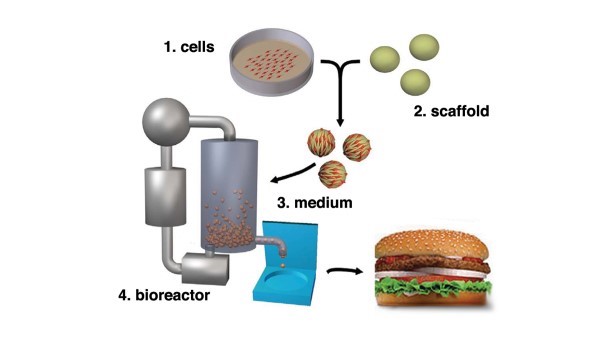
Scaling Up Production
Product development efforts are well underway across the globe. In 2016, for example, San Francisco-based Memphis Meats unveiled the first meatball produced with clean meat technology. In late 2018, Aleph Farms debuted the very first cell-cultured steak. Significant investments from Tyson Foods’ venture capital arm Tyson Ventures, Cargill, Bill Gates and Richard Branson — among others — are driving innovation in the field and helping startups to reduce costs and scale up production.
Cell-based meat could hit supermarket shelves within the next 5 years. Before that happens, stakeholders must confront a number of questions. Among those – Who will be the key regulators? How will the regulators work to ensure product safety? And will consumers actually want to eat hamburgers, chicken nuggets and fish fillets produced in such a novel way and perhaps pay a premium to do so?
The Regulatory Conversation
Cellular agriculture came to life in 2018 – from Capitol Hill to the halls of the FDA and USDA. Given the novelty of the production process, the regulators engaged stakeholders to think through an appropriate regulatory pathway for meat, poultry and seafood produced from cell cultures.
A recently issued Memorandum of Understanding (March 7, 2019) outlines the U.S. government’s current thinking regarding a proposed pathway for cell-based meat and poultry. The MOU provides that the FDA and USDA will jointly regulate human food produced using cell culture technology derived from cell lines of USDA-amenable species. In other words, cell-based meat and poultry will be subject to joint FDA-USDA oversight. Seafood products will generally be subject to FDA oversight (except in limited instances where the species is considered to be USDA-amenable, e.g., catfish). This builds on existing precedent as current American food law places the production and processing of meat and poultry under USDA jurisdiction. FDA regulates regulates all seafood except for Siluriformes (catfish) which fall under USDA oversight.
So what will joint regulation look like? The MOU indicates that the FDA will oversee cell collection, cell banks, and cell growth and differentiation. Oversight then shifts to the USDA during the cell harvest stage. USDA’s core tasks will be inspection and labeling. Upon harvest, USDA will conduct inspection activities at cell-based food processing facilities. This means that any establishment engaged in the business of processing harvested USDA-amenable, cell-based foods will need to obtain a federal grant of inspection from the USDA and all such foods will need to bear a USDA mark of inspection.
Many critical questions core to developing a functioning regulatory review process remain to be answered: How will the FDA and USDA initiate their respective application processes, how long will it take to obtain premarket approval, and what will inspections of production facilities look like? Further, how should these products be labeled? The devil will be in the details.
Regulators are currently reviewing comments submitted to the FDA and USDA following two public meetings: (1) An FDA meeting held on July 12, 2018 focused on safety considerations and (2) A joint FDA-USDA meeting held on October 23 and 24, 2018 focused on potential hazards and labeling.
Safety Considerations & Potential Hazards
Regulators are focused on working with stakeholders to:
- Consider and develop appropriate controls for potential hazards that may arise during all stages of production, i.e., culturing and harvesting, processing, and packaging.
- Understand the safety profile of the cell culture media used to produce cell-based foods.
- Leverage best practices from the traditional meat, poultry and seafood production context, as well as the biomedical arena as appropriate, to ensure that meat and poultry produced by way of cellular agriculture are safe and wholesome.
- Consider how these products will compare to traditionally produced meat and poultry from a compositional, nutritional and organoleptic standpoint.
Based on our conversations with cell-based meat producers, it is clear that in many cases the production process for cell-based foods will likely not be vertically integrated. That is, each step in the production process could be an end point — i.e., the collection, characterization and qualification of cell-lines could be conducted by Company A; Company B could then grow the meat in a cultivator (bioreactor) with media supplied by Company C; Company D could, in turn, market the meat once harvested at Company B. Hazards could conceivably emerge at each step, and especially during the transportation phase. Thus, regulators and producers will need to consider those transitions and outline where hazard control responsibilities begin and end and how best the FDA and/or USDA should go about verifying compliance.
Labeling
As of this writing, no set nomenclature has been settled upon for meat, poultry or seafood produced through cellular agriculture.
The labeling of cell-based meat and poultry is a hot button issue that came to the forefront in February 2018. That month, the United States Cattlemen’s Association (USCA) filed a petition with USDA’s Food Safety and Inspection Service (FSIS) requesting that USDA undertake rule-making on beef labeling to clarify the difference between beef derived from cattle and “beef” products created through cell culture technology. To date, the USDA has received over 6,100 comments on this petition.
Cell-based meat and conventional agriculture stakeholders have expressed a range of views. Among conventional animal agriculture interests, some contend that terms such as “meat” and “beef” should not be used to describe products produced through cellular agriculture. Others have expressed some openness to using “meaty” terms provided that the labeling clearly indicates how the product was produced. In this regard, some commenters called for the establishment of standards of identity for cell-cultured foods to distinguish them from their conventionally produced counterparts.
At a recent industry meeting and in recent industry trade press, USDA has indicated that the Agency is strongly considering proposing such standards of identity within the next 12 months.











